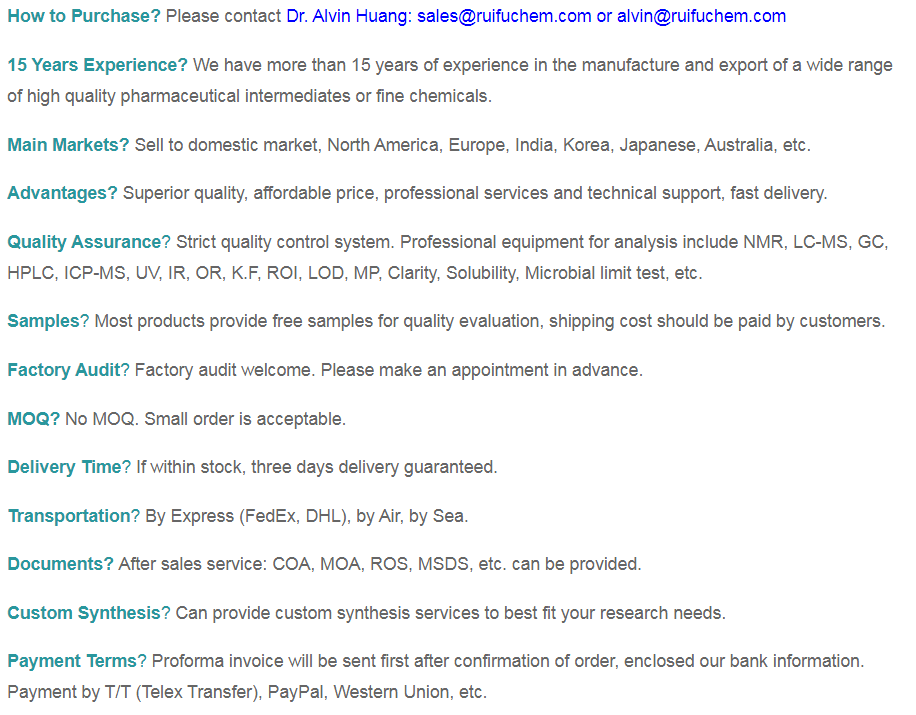
Methylboronic Acid CAS 13061-96-6 Purity >98.0% (Titration)
Manufacturer Supply With High Quality, Commercial Production
Chemical Name: Methylboronic Acid CAS: 13061-96-6
| Chemical Name | Methylboronic Acid |
| Synonyms | Methaneboronic Acid |
| CAS Number | 13061-96-6 |
| Stock Status | In Stock, Production Scale Up to Tons |
| Molecular Formula | CH5BO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 59.86 |
| Melting Point | 91.0~94.0℃(lit.) |
| Density | 0.965±0.06 g/cm3 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in Water |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| COA & MSDS | Available |
| Place of Origin | Shanghai, China |
| Brand | Ruifu Chemical |
| Item | Specifications | Results |
| Appearance | White Crystals | White Crystals |
| Methylboronic Acid Purity | >98.0% (Neutralization Titration) | 98.25% |
| Melting Point | 87.0~94.0℃ | 90.5℃ |
| Total Impurities | <2.00% | Conforms |
| Infrared Spectrum | Conforms to Structure | Conforms |
| 1H NMR Spectrum | Conforms to Structure | Conforms |
| Test Standard | Enterprise Standard | Conforms |
Package: Bottle, Aluminium foil bag, 25kg/Cardboard Drum, or according to customer's requirement.
Storage Condition: Store in sealed containers at cool and dry place; Protect from light and moisture.

Hazard Symbols Xi - Irritant
Risk Codes 36/37/38 - Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin.
Safety Description
S26 - In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
S36 - Wear suitable protective clothing.
WGK Germany 3
FLUKA BRAND F CODES 3-10
HS Code 2931900090
Hazard Note Irritant/Keep Cold
Hazard Class IRRITANT
Methylboronic Acid (CAS: 13061-96-6) is a methylated derivative of boronic acid, a building block towards various intermediates in suzuki coupling, has many applications in organic synthesis. Methylboronic Acid can be used as a reagent: In the palladium-catalyzed Stille and Suzuki-Miyaura cross-couplings. In the enantioselective asymmetric bromoaminocyclization and bromoaminocyclization using amino-thiocarbamate catalysts. To prepare common building blocks for pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. To prepare chrysin analogs by Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions. To prepare casein kinase I inhibitors. In the divergent C-H functionalizations directed by sulfonamide pharmacophores in drug discovery. In the synthesis of unsymmetrical monosulfides from disulfides via copper-catalyzed coupling with boronic acids. In a palladium-catalyzed coupling with enol tosylates. It is an important intermediate for the preparation of many boric acid derivatives.
-
Methylboronic Acid CAS 13061-96-6 Purity >98.0%...
-
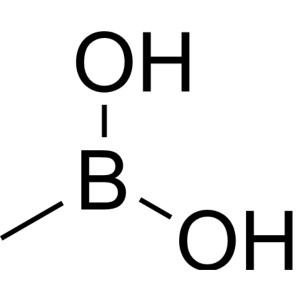
1-Naphthylboronic Acid CAS 13922-41-3 Purity >9...
-
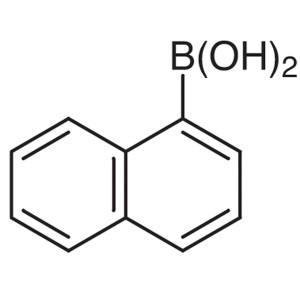
2-Naphthylboronic Acid CAS 32316-92-0 Purity >9...
-
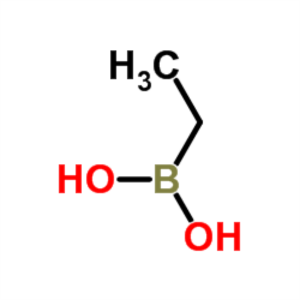
Ethylboronic Acid CAS 4433-63-0 Purity >98.0% (...
-
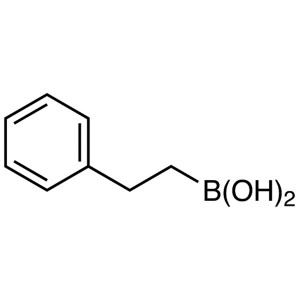
Phenethylboronic Acid CAS 34420-17-2 Purity >98...
-
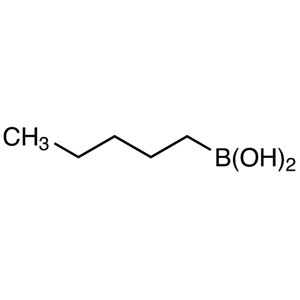
n-Pentylboronic Acid CAS 4737-50-2 Purity >98.0...
-
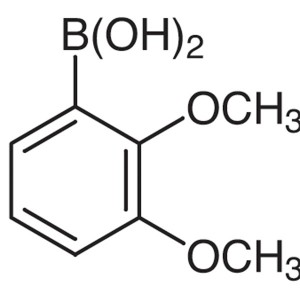
2,3-Dimethoxyphenylboronic Acid CAS 40972-86-9 ...
-
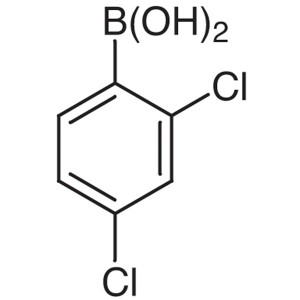
2,4-Dichlorophenylboronic Acid CAS 68716-47-2 P...
-
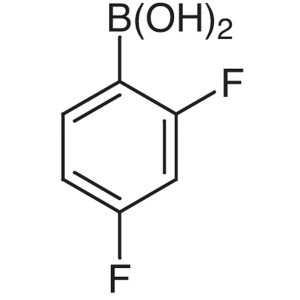
2,4-Difluorophenylboronic Acid CAS 144025-03-6 ...
-
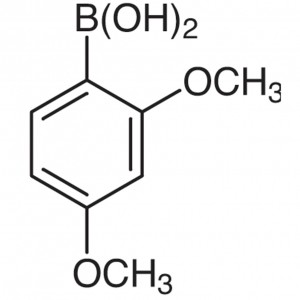
2,4-Dimethoxyphenylboronic Acid CAS 133730-34-4...
-
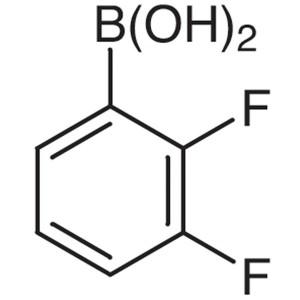
2,3-Difluorophenylboronic Acid CAS 121219-16-7 ...



